The relationship between gastrointestinal dysfunctions and systemic inflammatory diseases has been well known for decades, but there are not properly protocolized treatment approaches. A higher incidence of joint symptoms in patients affected by Inflammatory Bowel Disease is well known.
The small intestine plays an indispensable role in homeostasis; It is the main source of contact of the organism with the external environment and is subjected daily to a load of nutrients and foreign substances, potentially harmful; this defensive role is supported by the presence of immune cells residing in it, representing up to 70% of all systemic immune tissue. The tissue and functional basis of this function is determined by the intestinal barrier, and it is formed by the enterocytes with their intercellular junctions, the lamina propria and the associated lymphoid tissue. Under physiological conditions, this barrier prevents the passage of multiple intraluminal substances into the bloodstream through selective permeability.
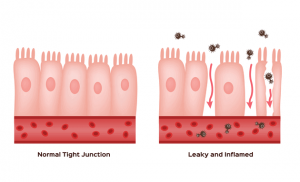
The integrity of this can be altered due to the ingestion of substances with high immunogenic power, the alteration of the intestinal microflora or the presence of elements that are essentially harmful to the mucosa such as NSAIDs, for example.
The mechanism by which intestinal permeability occurs is unknown, but there is evidence that it involves the immune system, intestinal flora and diet, fundamentally.
The human small intestine contains a high number of commensal bacteria, essential for adequate homeostasis. These microorganisms collaborate in turn in the integrity of the intestinal barrier.
The composition of the intestinal flora in cases of inflammatory disease of rheumatic origin (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis) is well documented, with an excessive proliferation of Klebsiella, Proteus and E.coli species. Another study shows that there is a different bacterial population in vegetarian individuals.
The presence of molecules recognized as foreign by the intestinal immune system would trigger an inflammatory cascade with the production of cytokines and free radicals that would contribute to producing and perpetuating damage to the integrity of the barrier.
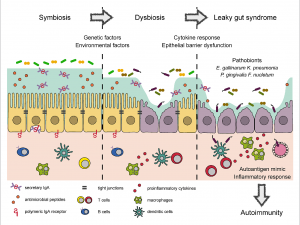
The concept of Leaky Gut Syndrome (LGS), in which there is a physical and functional disruption of the intestinal barrier because of which substances with high immunogenic power (bacterial and food residues) would enter the systemic circulation; this triggers a cascade of inflammatory mediators, related to the development of systemic diseases; These substances would come from the diet and from bacterial residues and antigens, fundamentally.
A clear relationship has been seen between gastrointestinal dysfunction, intestinal permeability, and intestinal dysbiosis, with highly prevalent pathologies such as fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue, or irritable bowel syndrome, which affects between 10 and 20% of the population.
Having a basic treatment that completely rebalances gastrointestinal function would be an important therapeutic advance, and a unique tool for professionals and patients, to reduce the impact of these important pathologies.